1 Introduction
Generative models have emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing image classifiers’ training process and interpretability. By synthesizing new images, these models can be employed for data augmentation, particularly in scenarios where certain classes are underrepresented. This oversampling technique has been shown to improve the performance of classifiers in various domains (Frid-Adar et al., 2018; Sankar et al., 2021). Moreover, generative models can aid in the interpretability of classifiers by producing counterfactual explanations (CEs) (Wachter et al., 2017). These CEs illustrate the necessary realistic changes in an image that would alter the classifier’s decision, providing valuable insights into the model’s decision-making process.
However, existing methods for generating CEs often rely on external models that operate independently of the classifier, introducing a semantic gap and significant complexity (Atad et al., 2022; Bedel and Çukur, 2023; Pegios et al., 2024; Fontanella et al., 2023). In this paper, we propose an approach that directly operates on the latent space of a single model, specifically a Diffusion Autoencoder (DAE) (Preechakul et al., 2022). Our method involves training the generative model to learn the data distribution in an unsupervised manner and then performing classification and regression tasks directly on the learned latent space.
By operating on the latent space of the DAE, our approach enables the inherent generation of CEs. These CEs provide a visual representation of the model’s decision boundaries and illustrate the characteristics of images on either side of this boundary. This is particularly useful for modeling a regression between two extremes of a pathology, such as vertebral compression fractures (VCFs). In this context, obtaining labels for the intermediate grades between visibly distinct extremes is challenging due to label scarcity and inter-rater-disagreement. Our method addresses this issue by leveraging the DAE’s continuous latent space to capture the pathology’s progression. We interpolate between latent representations of extreme cases to perform ordinal regression in this latent space, modeling the continuous progression of the pathology. Moreover, since the generative model is trained without supervision and since our method is not dependent on an external classifier, we can generate CEs matching multiple tasks on the same latent space without repeated training. Our contribution is three-fold:
- 1.
Inherent CE generation: The generative nature of DAE allows us to create images that resemble the model’s inner representation of different pathology grades. With this approach, we extend binary CEs to ordinal regression and aid interpretability by visualizing the change in the image parts that the model deems most important.
- 2.
Unsupervised feature extraction: We use unlabelled data to train a DAE model as an unsupervised feature extractor, this enables CE generation for multiple downstream tasks with the same learned latent space. Unlike previous methods that rely on separate models, our approach directly manipulates codes in the latent space, simplifying the process.
- 3.
Modelling pathology grading as a continuous regression: We employ a continuous regression approach in the latent space. We exemplify the strengths of this approach in modeling the smooth progression of pathologies such as intervertebral disc (IVD) degradation and diabetic retinopathy (DR) while requiring only binary labels.
2 Related works
2.1 Counterfactual explanations (CEs)
Counterfactual explanations (CEs), introduced by (Wachter et al., 2017), offer actionable insights by suggesting minimal changes to an input that would alter a model’s classification. Unlike gradient-based explainability methods such as saliency maps (Wang et al., 2017), which highlight influential features, CEs aim for changes that maintain realism and adherence to the data distribution, distinguishing them from adversarial attacks (Verma et al., 2020).
In medical imaging, CEs are invaluable for providing clinicians with insights into alternative diagnoses through plausible image modifications. This capability is critical for enhancing trust in diagnostic models by ensuring CEs remain within the medical data distribution. Generation of medical imaging CEs has evolved with the application of generative models like Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) (Cohen et al., 2021) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) (Singla et al., 2023; Atad et al., 2022; Schutte et al., 2021; Dravid et al., 2022). Recent advances in controlled image generation with Diffusion Models (Dhariwal and Nichol, 2021; Ho and Salimans, 2021) have introduced sophisticated methods for creating condition-specific CEs. Techniques including classifier-guided (Bedel and Çukur, 2023; Pegios et al., 2024) leverage gradients from pretrained classifier and ones using classifier-free guidance (Sanchez et al., 2022; Dhinagar et al., 2024; Fontanella et al., 2023) condition the generation process on labels or classifier saliency maps to produce CEs.
Our method stands out by utilizing a Diffusion Autoencoder (DAE) (Preechakul et al., 2022) for CE generation within the diffusion model’s latent space. This approach enables direct edits to latents, streamlining CE without needing external classifiers, and simplifying the process.
2.2 Generative self-supervision
Supervised Learning approaches have successfully solved many problems in image processing. Nevertheless, their dependency on the size of the annotated dataset is a significant obstacle in domains in which data annotation is time-consuming and relies on expert annotators. In Self-Supervised Learning (SSL), networks use unlabeled training data to learn meaningful feature representations through an auxiliary task, which are then used for downstream tasks.
Specifically in the generative SSL setting, it is common to synthesize novel examples with a generative model and use them as a dataset for training an external model for a downstream task, such as classification (Frid-Adar et al., 2018; Kitchen and Seah, 2017; Nie et al., 2017). Another line of work uses feature representations learned by the generative network itself for a discriminative task (Yi et al., 2018; Sankar et al., 2021).
Xu et al. (2021) demonstrated that latents learned by StyleGAN (Karras et al., 2020) can be used for downstream tasks such as regression and classification in a fully supervised manner. As a direct inspiration to our work, Nitzan et al. (2022) use StyleGAN latent codes to predict the magnitude of a visual attribute by measuring its distance from a hyperplane matching a linear direction with a semantic meaning. Preechakul et al. (2022) migrated this approach to Diffusion Models, thus circumventing GAN Inversion (Tov et al., 2021).
2.3 Ordinal regression in clinical applications
Medical image analysis requires distinguishing between binary classification, multiclass classification, ordinal regression, and regression. Binary classification differentiates between two distinct classes, such as the presence or absence of a pathology. Multiclass classification assigns cases to one of several categories without considering any order among them. In contrast, ordinal regression predicts a rank-ordered score that reflects the severity of a condition. Regression, on the other hand, predicts a continuous numerical value rather than discrete, ordered categories. While regression is used for predicting exact measurements, ordinal regression is used when the outcome is categorical but ordered, such as grading the severity of a disease. This ordered grading is crucial since it enables clinicians to monitor disease progression, adjust treatment plans, and prioritize cases based on severity (e.g., for DR (Flaxel et al., 2020)). Although this study focuses on ordinal regression, our method could also be applied to regression tasks where predicting a continuous outcome is required.
2.3.1 Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs)
We specifically study VCFs, the most prevalent osteoporotic fractures in those over 50, causing significant pain and disability (Ballane et al., 2017; Old and Calvert, 2004). Radiologists use the Genant scale (Genant et al., 1993) to measure fracture severity from CT images. Deep Learning can automate VCF detection (Valentinitsch et al., 2019; Tomita et al., 2018; Chettrit et al., 2020; Husseini et al., 2020b; Yilmaz et al., 2021; Engstler et al., 2022; Windsor et al., 2022; Iyer et al., 2023; Hempe et al., 2024), however, only a few works have considered VCF grading, all fully-supervised (Pisov et al., 2020; Zakharov et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2022; Yilmaz et al., 2023). Compared to fracture detection, grading is an even more imbalanced task since medium to severely fractured vertebrae account for only a small portion of overall data. Closest to our approach, Husseini et al. (2020a) and Hempe et al. (2024) train auto-encoders for vertebra shape reconstruction and then use the learned latent codes for downstream fracture detection.
3 Method
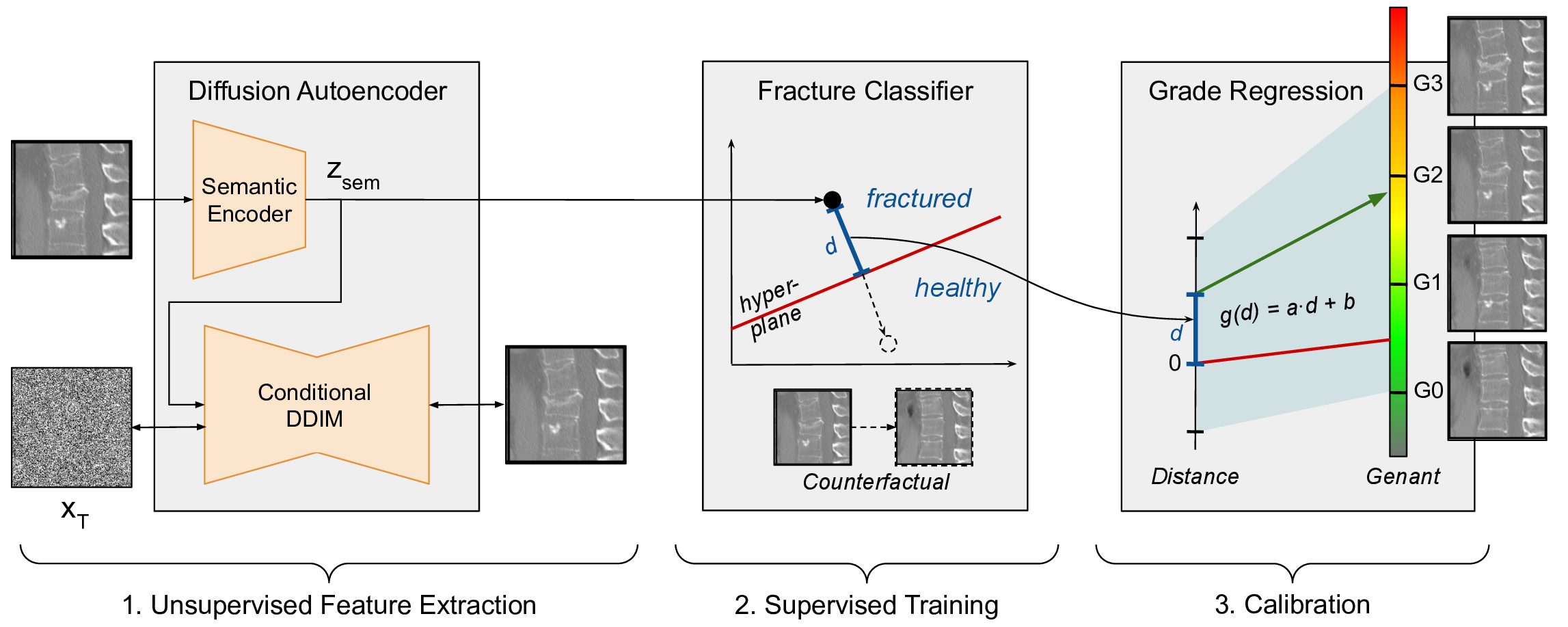
Our method involves three steps (Fig. 1). First, the generative DAE model is trained using unlabelled data. This model learns a compressed, semantically rich, latent space useful for downstream tasks. Next, labeled images are encoded into this latent space, and a linear classifier is trained on these labels. Finally, we use the classifier’s decision boundary to interpolate in latent space, edit images, create CEs, and rate pathologies.
3.1 Unsupervised feature extraction
We use DAE (Preechakul et al., 2022) as a generative unsupervised feature extractor. DAE leverages the capabilities of Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) (Sohl-Dickstein et al., 2015) and Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIMs) (Song et al., 2021) for unsupervised feature extraction. DAE distinguishes itself by incorporating a semantic encoder, designed to transform input images into a semantic latent space , that captures semantically meaningful information. This space is different from the DDPM and DDIM noise latent space , which was shown to lack high-level semantics (Kwon et al., 2023). Using enables the model to generate high-fidelity reconstructions and facilitate downstream tasks with a higher degree of semantic awareness. Moreover, it was shown that the semantic latent space is characterized by a linear data manifold, similar to StyleGAN’s StyleSpace (Preechakul et al., 2022), facilitating meaningful interpolation between latent representations.
The architecture of DAE is characterized by its use of conditional DDIM, which performs dual functions: it acts as a stochastic encoder to encode the input image into a noise representation and as a decoder to reconstruct the image from the combined semantic and noise latents. This method allows the model to effectively retain and utilize semantic details throughout image reconstruction. Training the DAE model involves minimizing the loss function:
| (1) |
where is the input image, is the timestep, is the noise component and is a neural network. Training the DDIM backbone and the semantic encoder simultaneously ensures that the model produces semantically meaningful and visually coherent outputs.
3.2 Linear decision boundary
We obtain the semantic latent representation for a subset of training samples for which labels are available and train linear classifiers (linear regression and SVM) to predict the existence of the target pathology. The decision boundary of a binary linear classifier is represented by the hyperplane given by its normal equation:
| (2) |
where is a semantic direction corresponding to the pathology existence, is an input image latent, and is a bias term. The magnitude of pathology in grading tasks is estimated using the distance of the latent to the hyperplane (Nitzan et al., 2022):
| (3) |
A simple linear regression is fitted to calibrate this distance to the respective pathology scale. Finally, the continuous values are rounded to the nearest grade to obtain the clinical grading in ordinal categories, matching the ground truths.
3.3 Counterfactual explanations
To generate CE images, the semantic latent code can be changed in the direction and together with the original stochastic latent decoded by the conditional DDIM to a new image. For binary CEs, we reflect a given latent sample to an equivalent position on the opposite side of the decision boundary, maintaining the original distance from the boundary within the latent space. For a latent sample , the counterfactual is:
| (4) |
To generate a counterfactual of a particular pathology grade, the calibration utilized in the regression process is inverted to determine the magnitude of the required change along the semantic direction.
4 Experiments
4.1 Datasets
| Dataset | Task | label 0 | label 1 | label 2 | label 3 | label 4 |
| VerSe | Genant grading | - | ||||
| SPIDER | Pfirrmann grading | |||||
| RetinaMNIST | Diabetic retinopathy severity | |||||
| BraTS | Peritumoral edema | - | - | - | ||
| MIMIC-CXR | Lung opacity | - | - | - | ||
| Pneumonia | - | - | - | |||
| Cardiomegaly | - | - | - | |||
| Edema severity grading | - |
We experimented with several ordinal regression and classification tasks, some suffering from high class-imbalance (Table 1).
Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs): We used the public VerSe dataset (Liebl et al., 2021; Sekuboyina et al., 2021) and an in-house dataset acquired at Klinikum Rechts der Isar and Klinikum der Universität München (Foreman et al., 2024), containing a total of 12019 sagittal 2D CT slices of vertebrae. Each slice has a size of pixels centered around a single vertebra, though multiple surrounding vertebrae are also visible. For each slice, the existence of a VCF in the center vertebra is indicated, and a small subset also includes a Genant grading, ranging from G0 (Normal/No fracture) to G3 (Severe/Over 40% reduction). Of the 1248 fractured samples, 220 have a grading (74 G1, 102 G2, 44 G3). We applied no image augmentations and kept other training parameters with their defaults. We only use samples from the VerSe dataset to train the fracture classifiers and evaluate their grading.
Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration: The SPIDER dataset (van der Graaf et al., 2024) contains a total of 1446 3D T2-weighted MRI volumes. We preprocess these volumes to extract a random 2D sagittal slice, each centered around a single IVD. Each IVD’s matching Pfirrmann grade (Pfirrmann et al., 2001) is indicated. The Pfirrmann grading system is a widely recognized scale for assessing the degree of IVD degeneration in MRI. It ranges from Grade I, indicating no degeneration with a homogeneous structure and normal disc height, to Grade V, which signifies severe degeneration with a collapsed disc space and inhomogeneous structure with areas of hypointensity.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR): The RetinaMNIST dataset (Yang et al., 2023) comprises 1200 pixel Fundus camera images, each labeled with its corresponding DR severity grade. DR is a diabetes complication that affects the eyes and is characterized by damage to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina). The severity of DR is categorized into five stages: from Grade 0 (no DR), representing no apparent retinal damage, to Grade 4 (proliferative DR), indicating advanced disease with a high risk of vision loss. Due to the small size of the dataset, we further applied image augmentation while training the DAE: image rotation (), image flip, grid distortion, and zoom (), each with a probability of .
Peritumoral edema in brain tumors: The BraTS dataset (Menze et al., 2014) consists of 484 3D FLAIR T2-weighted MRI volumes. In the preprocessing step, we extract a random 2D slice from each volume and a binary label indicating the presence of peritumoral edema in each slice. This condition represents fluid accumulation around the tumor site, often indicative of the tumor’s aggressiveness and the body’s response to its presence.
Cardiomegaly, lung opacity, pneumonia and edema in chest X-rays: The MIMIC-CXR dataset (Johnson et al., 2019) is an extensive collection of chest radiographs labeled to reflect common conditions that can be identified through radiographic imaging. In the preprocessing step, each chest X-ray image is resized to a resolution to standardize input size across the dataset. The DAE was trained on 166512 unlabeled images. For training the classifiers, we chose a subset of labeled anterior-posterior (AP) images for lung edema, opacity, pneumonia, and cardiomegaly and used labels extracted from reports by the CheXbert (Smit et al., 2020) labeler. The severity grades for the ordinal regression of edema are taken from Horng et al. (2021) following their dataset splits.
4.2 Implementation details
We trained the DAE for steps with a batch size of on a single Nvidia A40 GPU. We used the official DAE implementation by Preechakul et al. (2022). The semantic encoder used codes of . To encode images and create CEs, reverse diffusion steps were used to encode the images back to the stochastic latent . The stochastic latent was then concatenated to the semantic latent in forward diffusion steps to retrieve the original image . More training hyper-parameters are given in Sec. Appendix. All grades apart from the minimal are considered positive for training the SVM and linear regression classifiers. For VCFs, since the labels were noisy, only G2 and G3 were considered as the positive class. For the image reconstruction baseline, we used StyleGAN2 (Karras et al., 2020) with Encoder4Editing (E4E) (Tov et al., 2021). For the classification and regression baseline, we used DenseNet121 and trained it from scratch with the same data pipeline.
4.3 Evaluation metrics
To evaluate image reconstruction, we measure the perceptual similarity between the original and encoded image using Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) and the general image generation quality using the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID). For classification performance we use ROC-AUC and score. We calculated the macro and Mean Average Error (MAE) for grading performance.
5 Results and discussion
5.1 Image reconstruction
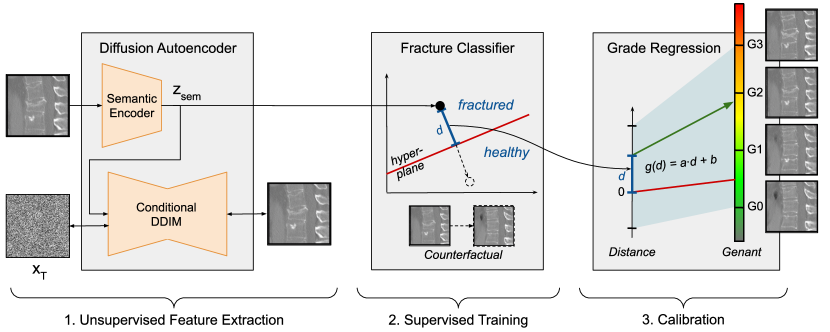
We begin by evaluating the DAE’s capability to accurately reconstruct images from latent codes using the VCF task. As shown in Table 2, the DAE semantic encoder outperforms StyleGAN2 E4E in reconstructing vertebrae images, as evidenced by LPIPS scores. Fig. 2 supports this finding, illustrating E4E’s limited ability to capture fracture-relevant features. Despite the overall similarity in appearance between the original and E4E-reconstructed images, the fracture cavity (highlighted in red) is mostly lost. Additionally, the FID measurements in Table 2 demonstrate that DAE generates higher-quality image distributions.
| Model | Encoder | Encoding (LPIPS ) | Generation (FID ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| StyleGAN2 | E4E | ||
| DAE | DAE encoder |
5.2 Discriminative tasks
We conduct extensive experiments to measure the discriminative capability of the DAE latents in detection and regression in multiple tasks. For VCFs, Table 3 shows that both linear layers and SVM can effectively separate fractured from healthy vertebrae by constructing a separating hyperplane with a respective AUC of 0.96 and 0.93. Results reported by Husseini et al. (2020a) further highlight the advantages of DAE as a feature extractor in comparison to Autoencoder (AE) and Variational Autoencoder (VAE). Although the linear layer achieves better detection results, the SVM’s hyperplane shows better performance in the linear regression of Genant grades. In Table 4, our method achieved comparable results to a fully supervised DenseNet121 baseline on other detection tasks.
| Model | Encoder | Classifier | Detection (AUC ) | Grading ( ) |
| Linear probing trained on G0, G2 and G3 with frozen encoder of generative model | ||||
| AE (Husseini et al., 2020a) | AE | Linear layer | - | |
| VAE (Husseini et al., 2020a) | VAE | Linear layer | - | |
| Spine-VAE (Husseini et al., 2020a) | VAE | Linear layer | - | |
| 3D point-cloud (Hempe et al., 2024) | AE | MLP | - | |
| StyleGAN2 | E4E | SVM | - | |
| DAE | DAE | Linear layer | 0.96 | (0.23) |
| DAE | DAE | SVM | 0.93 | 0.59 |
| Linear regression with distance to the hyperplane, calibrated with means of G0 and G3 | ||||
| DAE | DAE | Linear layer | 0.96 | 0.44 |
| DAE | DAE | SVM | 0.93 | 0.51 |
| Polynomial regression with distance to hyperplane, calibrated with G0, G2 and G3 | ||||
| DAE | DAE | SVM (deg=1) | 0.93 | 0.42 |
| DAE | DAE | SVM (deg=3) | 0.93 | 0.56 |
| End-to-end training with full supervision (G0, G2 and G3) | ||||
| DenseNet121, baseline | ||||
| 3D SE-ResNet50 with SupCon loss (Wei et al., 2022) | ||||
| Model | Dataset | Task (# labels) | Detection | Grading | ||
| AUC | MAE | |||||
| DAE, SVM classifier | Spider | Pfirrmann grade, ordinal (5) | ||||
| DAE, LR classifier | ||||||
| DenseNet121 | ||||||
| DAE, SVM classifier | RetinaMNIST | Diabetic retinopathy severity, ordinal (5) | ||||
| DAE, LR classifier | ||||||
| DenseNet121 | ||||||
| DAE, SVM classifier | BraTS | Peritumoral edema, binary (2) | - | - | ||
| DAE, LR classifier | - | - | ||||
| DenseNet121 | - | - | ||||
| DAE, SVM classifier | MIMIC-CXR | Edema severity grade, ordinal (4) | ||||
| DAE, LR classifier | - | - | ||||
5.3 Counterfactual explanations
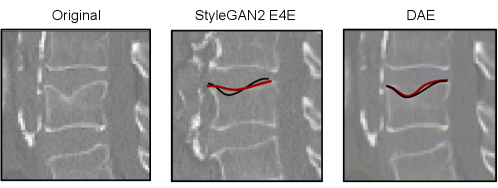
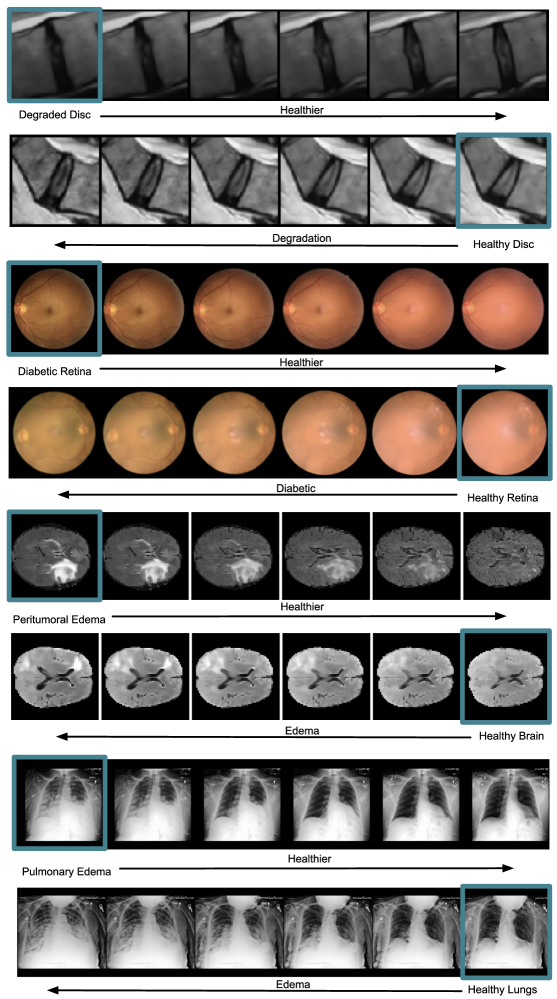
Besides feature extraction, our method provides inherent CE generation. In this setting, the generative capability of the model can aid the interpretability of the decision support system. In Fig. 3, the input image (left), after being encoded into the latent space (center), can be manipulated towards both classes, e.g., from healthy vertebra to severe fracture and vice versa. Similarly, in Fig. 4, the input image (in the blue box) is manipulated towards the opposite class relative to the binary decision boundary, i.e., from healthy to pathology and vice versa.
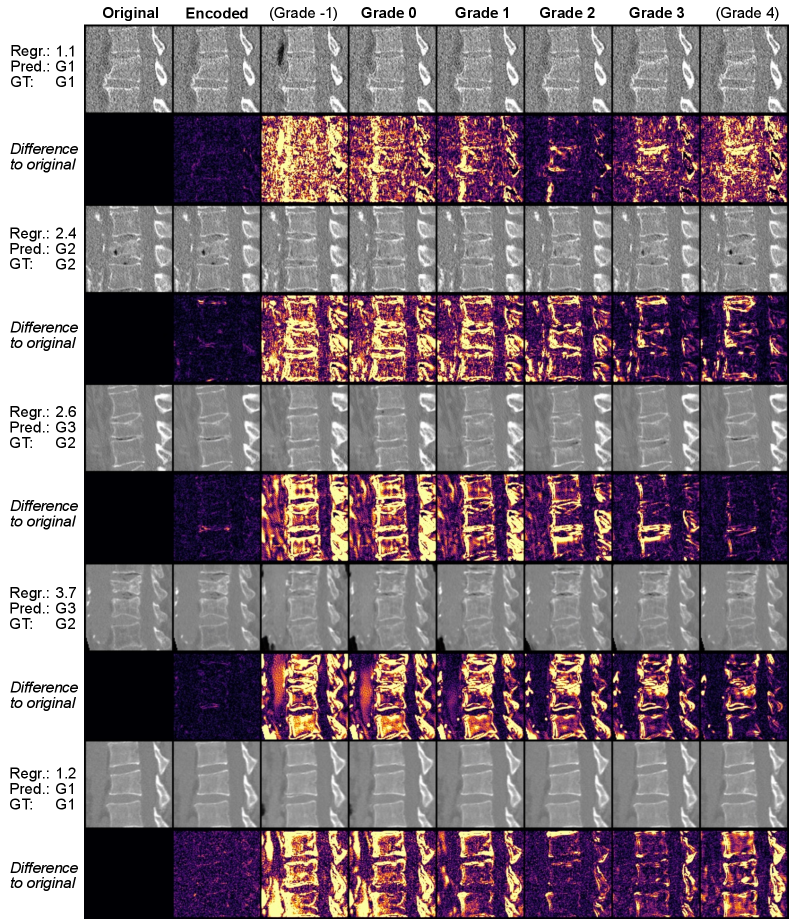
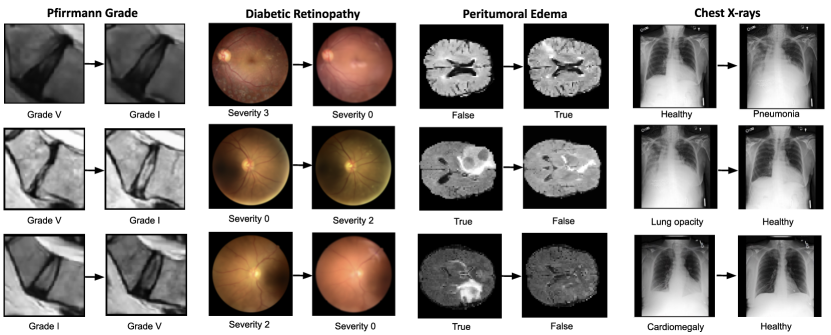
Fig. 5 demonstrates that our CEs can be extended to visualize whether the model is well calibrated to the ordinal regression of Genant grades by showing the model’s perception of each grade for a given vertebra. While the last row in Fig. 5 is not well calibrated, the rightmost image augments a barely visible feature. This exaggeration of anatomical changes could guide the radiologist’s attention and help estimate the potential progression of pathological changes barely visible in the original image.
Additional examples in Fig. 6 highlight the limitations of our method. A qualitative evaluation by a clinician revealed several issues: The Pfirrmann grade V CE shows only a slight signal loss with minimal height loss, suggesting it should be graded as grade II. In the DR examples, the model introduces additional blurring when transitioning from diseased to healthy states. The removal of peritumoral edema is only partial in the second case. Additionally, in the same task, clinicians noted size changes between the CEs and the original images, indicating a potential model bias related to the MRI slice position along the axial plane.
5.4 Limitations and future work
5.4.1 Discriminative tasks
While the well-calibrated samples in Fig. 5 show impressive visual results, the VCF grading metrics in Table 3 reveal the limitations of our method. The linear separability of classes in DAE’s semantic latent space using 2D slices cannot compete with the fully supervised, end-to-end baseline and 3D methods, motivating an extension to three dimensions.
One reason for this might be a failure to disentangle the fracture of adjacent vertebrae from the central vertebral body that is classified. This can be observed in the second to last example in Fig. 5, where the center vertebra remains unchanged while the top one changes with the severity of the fracture. At the same time, this showcases the interpretability of our approach by visualizing the model’s understanding of different grades, highlighting its misguided feature attribution. In future work, the network could be explicitly guided to attend to the central vertebrae, or the generation process could be conditioned on anatomical features, thus disentangling these from disease progression.
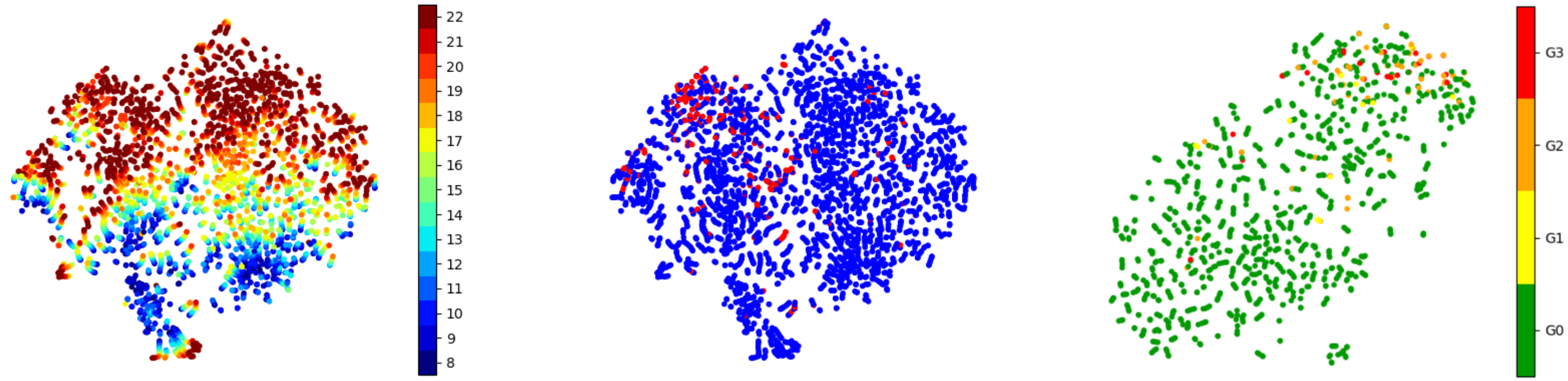
The t-SNE projection of latents in Fig. 7 clearly shows that the unsupervised DAE clustered the vertebral levels ranging from T1 to L5. Since fractures occur more frequently in the lumbar spine, a cluster of fractures can be observed there with many outliers. We hypothesized that training with all levels could aid the data imbalance since only very few fractures are present in the data per vertebral level. However, the better separatability of Genant grading in the visually similar subset of vertebra L1-L4 (Fig. 7, right) suggests investigating independent models for the different spine segments.

To challenge the assumption of a linear relationship between the distance to the hyperplane and the severity of the fracture, we fitted a polynomial regression to grades G0, G2, and G3. The results in Table 3 show an improvement over our simple regression model, indicating the presence of a non-linear relationship that warrants further investigation in future research.
5.4.2 Counterfactual explanations
This work has demonstrated how CEs can reveal model biases by uncovering the inner representations of different classes and regression scores. For instance, manipulating vertebral images towards the healthy direction introduced a lung artifact, effectively translocating the vertebrae upwards within the spine where fractures are uncommon (Fig. 3). Another example is the bias related to brain slice position along the axial plane and the presence of edema (Fig. 4).
Beyond revealing such model biases, CEs offer crucial insights into AI models, lifting the ”black box” and empowering clinicians (and researchers) to understand the models’ inner decision-making. Further, CEs might potentially drive the discovery of novel imaging biomarkers (Kumar et al., 2022).
Future studies should validate the clinical applications of CEs based on DAE. These studies should focus on several key areas. First, they should explore the potential of CEs for imaging biomarker discovery by unveiling which features drive classification. Second, researchers should assess whether generated CEs can effectively demonstrate potential disease progression, helping clinicians anticipate future developments. Third, studies could investigate using CEs to visualize reverse disease progression, e.g. aiding in planning reconstructive surgeries such as bone cement filling in vertebral bodies. Lastly, these investigations should aim to identify model biases, ultimately improving the overall reliability of the algorithm in real-world clinical settings. Through these diverse applications, CEs could provide valuable insights into disease mechanisms and treatment planning while enhancing the interpretability and trustworthiness of AI models in clinical practice.
6 Conclusion
We present a methodological framework for generating counterfactual explanations (CEs) in medical imaging using Diffusion Autoencoders (DAE). By directly manipulating the latent space, our approach avoids the need for external classifiers, simplifying the generation process. Our findings highlight the versatility and interpretability of the DAE model across various medical imaging tasks, proving effective in classification and regression.
Moreover, this work demonstrates how CEs can uncover model biases. Future work will focus on the clinical validation of CEs to assess their practical applications, such as the discovery of imaging biomarkers and guiding treatment decisions. Additionally, we aim to address the study’s limitations, particularly in extending the model to three-dimensional data and disentangling the disease progression from anatomical features in the CE generation process.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research of Germany (BMBF) under project DIVA (FKZ 13GW0469C) and from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (101045128—iBack-epic—ERC2021-COG).
Ethical Standards
The work follows appropriate ethical standards in conducting research and writing the manuscript, following all applicable laws and regulations regarding treatment of animals or human subjects.
Conflicts of Interest
JK is co-founder of Bonescreen GmbH. The remaining authors declare the research was conducted in the absence of conflicts of interest.
Data availability
The majority of data used for this study is publicly available on the respective challenge’s website, allowing for reproduction of our results. We further used an internal dataset of unlabeled spine CTs for the VCF task, which could not be shared due to patient privacy.
References
- Atad et al. (2022) Matan Atad, Vitalii Dmytrenko, Yitong Li, Xinyue Zhang, Matthias Keicher, Jan Kirschke, Bene Wiestler, Ashkan Khakzar, and Nassir Navab. Chexplaining in style: Counterfactual explanations for chest x-rays using stylegan. arXiv:2207.07553, 2022.
- Ballane et al. (2017) Ghada Ballane, JA Cauley, MM Luckey, and G El-Hajj Fuleihan. Worldwide prevalence and incidence of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Osteoporosis International, 28(5):1531–1542, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-3909-3.
- Bedel and Çukur (2023) Hasan Atakan Bedel and Tolga Çukur. Dreamr: Diffusion-driven counterfactual explanation for functional mri. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09547, 2023.
- Chettrit et al. (2020) David Chettrit, Tomer Meir, Hila Lebel, Mila Orlovsky, Ronen Gordon, Ayelet Akselrod-Ballin, and Amir Bar. 3d convolutional sequence to sequence model for vertebral compression fractures identification in ct. In MICCAI, pages 743–752. Springer, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_72.
- Cohen et al. (2021) Joseph Paul Cohen, Rupert Brooks, Sovann En, Evan Zucker, Anuj Pareek, Matthew P Lungren, and Akshay Chaudhari. Gifsplanation via latent shift: a simple autoencoder approach to counterfactual generation for chest x-rays. In Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, pages 74–104. PMLR, 2021.
- Dhariwal and Nichol (2021) Prafulla Dhariwal and Alexander Nichol. Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. Advances in neural information processing systems, 34:8780–8794, 2021.
- Dhinagar et al. (2024) Nikhil J Dhinagar, Sophia I Thomopoulos, Emily Laltoo, and Paul M Thompson. Counterfactual mri generation with denoising diffusion models for interpretable alzheimer’s disease effect detection. bioRxiv, pages 2024–02, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.02.05.578983.
- Dravid et al. (2022) Amil Dravid, Florian Schiffers, Boqing Gong, and Aggelos K Katsaggelos. medxgan: Visual explanations for medical classifiers through a generative latent space. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2936–2945, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00331.
- Engstler et al. (2022) Paul Engstler, Matthias Keicher, David Schinz, Kristina Mach, Alexandra S Gersing, Sarah C Foreman, Sophia S Goller, Juergen Weissinger, Jon Rischewski, Anna-Sophia Dietrich, et al. Interpretable vertebral fracture diagnosis. In Interpretability of Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Computing (iMIMIC), pages 71–81. Springer, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17976-1_7.
- Flaxel et al. (2020) Christina J Flaxel, Ron A Adelman, Steven T Bailey, Amani Fawzi, Jennifer I Lim, G Atma Vemulakonda, and Gui-shuang Ying. Diabetic retinopathy preferred practice pattern®. Ophthalmology, 127(1):P66–P145, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.09.025.
- Fontanella et al. (2023) Alessandro Fontanella, Grant Mair, Joanna Wardlaw, Emanuele Trucco, and Amos Storkey. Diffusion models for counterfactual generation and anomaly detection in brain images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02062, 2023.
- Foreman et al. (2024) Sarah C Foreman, David Schinz, Malek El Husseini, Sophia S Goller, Jürgen Weißinger, Anna-Sophia Dietrich, Martin Renz, Marie-Christin Metz, Georg C Feuerriegel, Benedikt Wiestler, et al. Deep learning to differentiate benign and malignant vertebral fractures at multidetector ct. Radiology, 310(3):e231429, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.231429.
- Frid-Adar et al. (2018) Maayan Frid-Adar, Eyal Klang, Michal Amitai, Jacob Goldberger, and Hayit Greenspan. Synthetic data augmentation using gan for improved liver lesion classification. In ISBI, pages 289–293. IEEE, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2018.8363576.
- Genant et al. (1993) Harry K Genant, Chun Y Wu, Cornelis Van Kuijk, and Michael C Nevitt. Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. JBMR, 8(9):1137–1148, 1993. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.5650080915.
- Hempe et al. (2024) Hellena Hempe, Alexander Bigalke, and Mattias Paul Heinrich. Shape matters: detecting vertebral fractures using differentiable point-based shape decoding. Information, 15(2):120, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15020120.
- Ho and Salimans (2021) Jonathan Ho and Tim Salimans. Classifier-free diffusion guidance. In NeurIPS 2021 Workshop on Deep Generative Models and Downstream Applications, 2021.
- Horng et al. (2021) Steven Horng, Ruizhi Liao, Xin Wang, Sandeep Dalal, Polina Golland, and Seth J Berkowitz. Deep learning to quantify pulmonary edema in chest radiographs. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, 3(2):e190228, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2021190228.
- Husseini et al. (2020a) Malek Husseini, Anjany Sekuboyina, Amirhossein Bayat, Bjoern H Menze, Maximilian Loeffler, and Jan S Kirschke. Conditioned variational auto-encoder for detecting osteoporotic vertebral fractures. In Computational Methods and Clinical Applications for Spine Imaging. CSI 2019, Proceedings 6, pages 29–38. Springer, 2020a. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39752-4_3.
- Husseini et al. (2020b) Malek Husseini, Anjany Sekuboyina, Maximilian Loeffler, Fernando Navarro, Bjoern H Menze, and Jan S Kirschke. Grading loss: a fracture grade-based metric loss for vertebral fracture detection. In MICCAI, pages 733–742. Springer, 2020b. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_71.
- Iyer et al. (2023) Sankaran Iyer, Alan Blair, Christopher White, Laughlin Dawes, Daniel Moses, and Arcot Sowmya. Vertebral compression fracture detection using imitation learning, patch based convolutional neural networks and majority voting. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 38:101238, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2023.101238.
- Johnson et al. (2019) Alistair EW Johnson, Tom J Pollard, Seth J Berkowitz, Nathaniel R Greenbaum, Matthew P Lungren, Chih-ying Deng, Roger G Mark, and Steven Horng. Mimic-cxr, a de-identified publicly available database of chest radiographs with free-text reports. Scientific data, 6(1):317, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0322-0.
- Karras et al. (2020) Tero Karras, Samuli Laine, Miika Aittala, Janne Hellsten, Jaakko Lehtinen, and Timo Aila. Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In CVPR, pages 8110–8119, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00813.
- Kitchen and Seah (2017) Andy Kitchen and Jarrel Seah. Deep generative adversarial neural networks for realistic prostate lesion mri synthesis. CoRR, abs/1708.00129, 2017.
- Kumar et al. (2022) Amar Kumar, Anjun Hu, Brennan Nichyporuk, Jean-Pierre R Falet, Douglas L Arnold, Sotirios Tsaftaris, and Tal Arbel. Counterfactual image synthesis for discovery of personalized predictive image markers. In MICCAI Workshop on Medical Image Assisted Blomarkers’ Discovery, pages 113–124. Springer, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19660-7_11.
- Kwon et al. (2023) Mingi Kwon, Jaeseok Jeong, and Youngjung Uh. Diffusion models already have a semantic latent space. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023.
- Liebl et al. (2021) Hans Liebl, David Schinz, Anjany Sekuboyina, Luca Malagutti, Maximilian T Löffler, Amirhossein Bayat, Malek El Husseini, Giles Tetteh, Katharina Grau, Eva Niederreiter, et al. A computed tomography vertebral segmentation dataset with anatomical variations and multi-vendor scanner data. Scientific Data, 8(1):284, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-01060-0.
- Menze et al. (2014) Bjoern H Menze, Andras Jakab, Stefan Bauer, Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, Keyvan Farahani, Justin Kirby, Yuliya Burren, Nicole Porz, Johannes Slotboom, Roland Wiest, et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (brats). IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 34(10):1993–2024, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694.
- Nie et al. (2017) Dong Nie, Roger Trullo, Jun Lian, Caroline Petitjean, Su Ruan, Qian Wang, and Dinggang Shen. Medical image synthesis with context-aware generative adversarial networks. In MICCAI, pages 417–425. Springer, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_48.
- Nitzan et al. (2022) Yotam Nitzan, Rinon Gal, Ofir Brenner, and Daniel Cohen-Or. Large: Latent-based regression through gan semantics. In CVPR, pages 19239–19249, June 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01864.
- Old and Calvert (2004) Jerry L Old and Michelle Calvert. Vertebral compression fractures in the elderly. American family physician, 69(1):111–116, 2004.
- Pegios et al. (2024) Paraskevas Pegios, Manxi Lin, Nina Weng, Morten Bo Søndergaard Svendsen, Zahra Bashir, Siavash Bigdeli, Anders Nymark Christensen, Martin Tolsgaard, and Aasa Feragen. Diffusion-based iterative counterfactual explanations for fetal ultrasound image quality assessment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.08700, 2024.
- Pfirrmann et al. (2001) Christian WA Pfirrmann, Alexander Metzdorf, Marco Zanetti, Juerg Hodler, and Norbert Boos. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. spine, 26(17):1873–1878, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200109010-00011.
- Pisov et al. (2020) Maxim Pisov, Vladimir Kondratenko, Alexey Zakharov, Alexey Petraikin, Victor Gombolevskiy, Sergey Morozov, and Mikhail Belyaev. Keypoints localization for joint vertebra detection and fracture severity quantification. In MICCAI, pages 723–732. Springer, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_70.
- Preechakul et al. (2022) Konpat Preechakul, Nattanat Chatthee, Suttisak Wizadwongsa, and Supasorn Suwajanakorn. Diffusion autoencoders: Toward a meaningful and decodable representation. In CVPR, pages 10619–10629, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01036.
- Sanchez et al. (2022) Pedro Sanchez, Antanas Kascenas, Xiao Liu, Alison Q O’Neil, and Sotirios A Tsaftaris. What is healthy? generative counterfactual diffusion for lesion localization. In MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, pages 34–44. Springer, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18576-2_4.
- Sankar et al. (2021) Aadhithya Sankar, Matthias Keicher, Rami Eisawy, Abhijeet Parida, Franz Pfister, Seong Tae Kim, and Nassir Navab. Glowin: A flow-based invertible generative framework for learning disentangled feature representations in medical images. arXiv:2103.10868, 2021.
- Schutte et al. (2021) Kathryn Schutte, Olivier Moindrot, Paul Hérent, Jean-Baptiste Schiratti, and Simon Jégou. Using stylegan for visual interpretability of deep learning models on medical images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.07563, 2021.
- Sekuboyina et al. (2021) Anjany Sekuboyina, Malek E Husseini, Amirhossein Bayat, Maximilian Löffler, Hans Liebl, Hongwei Li, et al. Verse: A vertebrae labelling and segmentation benchmark for multi-detector ct images. Medical image analysis, 73:102166, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102166.
- Singla et al. (2023) Sumedha Singla, Motahhare Eslami, Brian Pollack, Stephen Wallace, and Kayhan Batmanghelich. Explaining the black-box smoothly—a counterfactual approach. Medical Image Analysis, 84:102721, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102721.
- Smit et al. (2020) Akshay Smit, Saahil Jain, Pranav Rajpurkar, Anuj Pareek, Andrew Ng, and Matthew Lungren. Combining automatic labelers and expert annotations for accurate radiology report labeling using BERT. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 1500–1519. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.117.
- Sohl-Dickstein et al. (2015) Jascha Sohl-Dickstein, Eric Weiss, Niru Maheswaranathan, and Surya Ganguli. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pages 2256–2265. PMLR, 2015.
- Song et al. (2021) Jiaming Song, Chenlin Meng, and Stefano Ermon. Denoising diffusion implicit models. In ICLR, 2021.
- Tomita et al. (2018) Naofumi Tomita, Yvonne Y Cheung, and Saeed Hassanpour. Deep neural networks for automatic detection of osteoporotic vertebral fractures on ct scans. Computers in biology and medicine, 98:8–15, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.05.011.
- Tov et al. (2021) Omer Tov, Yuval Alaluf, Yotam Nitzan, Or Patashnik, and Daniel Cohen-Or. Designing an encoder for stylegan image manipulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 40(4):1–14, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1145/3476576.3476706.
- Valentinitsch et al. (2019) A Valentinitsch, S Trebeschi, Johannes Kaesmacher, C Lorenz, MT Löffler, C Zimmer, T Baum, and JS Kirschke. Opportunistic osteoporosis screening in multi-detector ct images via local classification of textures. Osteoporosis international, 30(6):1275–1285, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-04910-1.
- van der Graaf et al. (2024) Jasper W van der Graaf, Miranda L van Hooff, Constantinus FM Buckens, Matthieu Rutten, Job LC van Susante, Robert Jan Kroeze, Marinus de Kleuver, Bram van Ginneken, and Nikolas Lessmann. Lumbar spine segmentation in mr images: a dataset and a public benchmark. Scientific Data, 11(1):264, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03090-w.
- Verma et al. (2020) Sahil Verma, Varich Boonsanong, Minh Hoang, Keegan E Hines, John P Dickerson, and Chirag Shah. Counterfactual explanations and algorithmic recourses for machine learning: A review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.10596, 2020.
- Wachter et al. (2017) Sandra Wachter, Brent Mittelstadt, and Chris Russell. Counterfactual explanations without opening the black box: Automated decisions and the gdpr. Harv. JL & Tech., 31:841, 2017. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3063289.
- Wang et al. (2017) Xiaosong Wang, Yifan Peng, Le Lu, Zhiyong Lu, Mohammadhadi Bagheri, and Ronald M Summers. Chestx-ray: Hospital-scale chest x-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 2097–2106, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13969-8_18.
- Wei et al. (2022) Xin Wei, Huaiwei Cong, Zheng Zhang, Junran Peng, Guoping Chen, and Jinpeng Li. Faint features tell: Automatic vertebrae fracture screening assisted by contrastive learning. In BIBM, pages 848–853, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2208.10698.
- Windsor et al. (2022) Rhydian Windsor, Amir Jamaludin, Timor Kadir, and Andrew Zisserman. Context-aware transformers for spinal cancer detection and radiological grading. In MICCAI, pages 271–281. Springer, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_26.
- Xu et al. (2021) Yinghao Xu, Yujun Shen, Jiapeng Zhu, Ceyuan Yang, and Bolei Zhou. Generative hierarchical features from synthesizing images. In CVPR, pages 4432–4442, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00441.
- Yang et al. (2023) Jiancheng Yang, Rui Shi, Donglai Wei, Zequan Liu, Lin Zhao, Bilian Ke, Hanspeter Pfister, and Bingbing Ni. Medmnist v2-a large-scale lightweight benchmark for 2d and 3d biomedical image classification. Scientific Data, 10(1):41, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01721-8.
- Yi et al. (2018) Xin Yi, Ekta Walia, and Paul Babyn. Unsupervised and semi-supervised learning with categorical generative adversarial networks assisted by wasserstein distance for dermoscopy image classification. arXiv:1804.03700, 2018.
- Yilmaz et al. (2023) Eren B Yilmaz, Tobias Fricke, Julian Laue, Constanze Polzer, Sam Sedaghat, Jan-Bernd Hövener, Claus-Christian Glüer, and Carsten Meyer. Towards fracture risk assessment by deep-learning-based classification of prevalent vertebral fractures. In Medical Imaging 2023: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, volume 12465, pages 304–311. SPIE, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2653526.
- Yilmaz et al. (2021) Eren Bora Yilmaz, Christian Buerger, Tobias Fricke, Md Motiur Rahman Sagar, Jaime Peña, Cristian Lorenz, Claus-Christian Glüer, and Carsten Meyer. Automated deep learning-based detection of osteoporotic fractures in ct images. In MLMI, pages 376–385. Springer, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87589-3_39.
- Zakharov et al. (2023) Alexey Zakharov, Maxim Pisov, Alim Bukharaev, Alexey Petraikin, Sergey Morozov, Victor Gombolevskiy, and Mikhail Belyaev. Interpretable vertebral fracture quantification via anchor-free landmarks localization. Medical Image Analysis, 83:102646, 2023. ISSN 1361-8415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102646.
Appendix
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 465 |
| Median age (years) | 69 (12) |
| Scan types | Healthy and fractured vertebrae |
| Nature of fractures | Osteoporotic or malignant |
| Additional features | Metallic implants and foreign materials |
| CT scanner | Heterogeneous |
| Scanner setting | Heterogeneous |
| Field of view | Varying |
| Library | Version |
|---|---|
| python | 3.9.15 |
| torch | 1.8.1 |
| torchvision | 0.9.1 |
| monai | 1.0.1 |
| pytorch-lightning | 1.4.5 |
| torchmetrics | 0.5.0 |
| scipy | 1.5.4 |
| numpy | 1.19.5 |
| pytorch-fid | 0.2.0 |
| lpips | 0.1.4 |
| pandas | 1.1.5 |
| Pillow | 8.3.1 |
| lmdb | 1.2.1 |
| cuml | 22.10.1 |
| scikit-learn | 1.1.3 |
| scikit-image | 0.19.3 |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| learning rate | 0.0001 |
| batch_size | 64 |
| image_size | 96 x 96 |
| embedding_size | 512 |
| eval_every_samples | 250,000 |
| precision | half |
| latent_T_eval | 1,000 |
| latent_beta_scheduler | linear |
| total_samples | 12,000,000 |
| T | 1,000 |
| eval_T | 20 |
| generation T | 100 |