Atlas-Based Interpretable Age Prediction In Whole-Body MR Images
Sophie Starck1 , Yadunandan Vivekanand Kini1
, Yadunandan Vivekanand Kini1 , Jessica J. M. Ritter2
, Jessica J. M. Ritter2 , Rickmer Braren1,2,3
, Rickmer Braren1,2,3 , Daniel Rueckert1,4
, Daniel Rueckert1,4 , Tamara T. Mueller1
, Tamara T. Mueller1
1: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare and Medicine, School of Computation, Information and Technology, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 2: Institute of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Technical University of Munich, School of Medicine, Munich, Germany, 3: German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), Munich partner site, Heidelberg, Germany, 4: BioMedIA, Department of Computing, Imperial College London, UK
Publication date: 2024/11/26
https://doi.org/10.59275/j.melba.2024-682e
Abstract
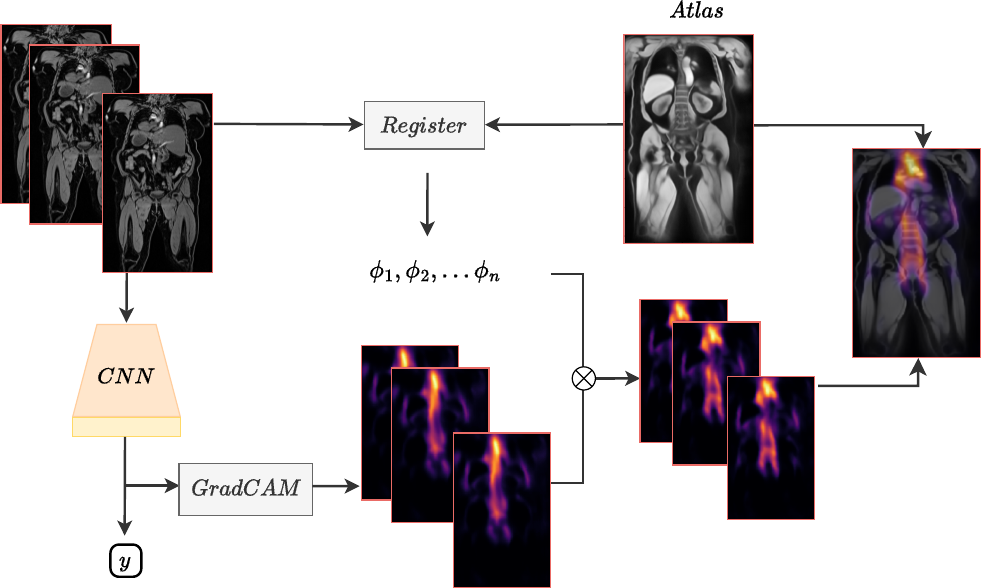
Age prediction is an important part of medical assessments and research. It can aid in detecting diseases as well as abnormal ageing by highlighting potential discrepancies between chronological and biological age. To improve understanding of age-related changes in various body parts, we investigate the ageing of the human body on a large scale by using whole-body 3D images. We utilise the Grad-CAM method to determine the body areas most predictive of a person’s age. In order to expand our analysis beyond individual subjects, we employ registration techniques to generate population-wide importance maps that show the most predictive areas in the body for a whole cohort of subjects. We show that the investigation of the full 3D volume of the whole body and the population-wide analysis can give important insights into which body parts play the most important roles in predicting a person’s age. Our findings reveal three primary areas of interest: the spine, the autochthonous back muscles, and the cardiac region, which exhibits the highest importance. Finally, we investigate differences between subjects that show accelerated and decelerated ageing.
Keywords
Age prediction · Medical atlases · UK Biobank
Bibtex
@article{melba:2024:029:starck,
title = "Atlas-Based Interpretable Age Prediction In Whole-Body MR Images",
author = "Starck, Sophie and Kini, Yadunandan Vivekanand and Ritter, Jessica J. M. and Braren, Rickmer and Rueckert, Daniel and Mueller, Tamara T.",
journal = "Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging",
volume = "2",
issue = "iMIMIC 2023 special issue",
year = "2024",
pages = "2247--2267",
issn = "2766-905X",
doi = "https://doi.org/10.59275/j.melba.2024-682e",
url = "https://melba-journal.org/2024:029"
}
RIS
TY - JOUR
AU - Starck, Sophie
AU - Kini, Yadunandan Vivekanand
AU - Ritter, Jessica J. M.
AU - Braren, Rickmer
AU - Rueckert, Daniel
AU - Mueller, Tamara T.
PY - 2024
TI - Atlas-Based Interpretable Age Prediction In Whole-Body MR Images
T2 - Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging
VL - 2
IS - iMIMIC 2023 special issue
SP - 2247
EP - 2267
SN - 2766-905X
DO - https://doi.org/10.59275/j.melba.2024-682e
UR - https://melba-journal.org/2024:029
ER -